[adsense:responsibe:9545213979]
Apartada a) de la cuestion 2 EDiferenciales 1206S2 (Ecuacion diferencial lineal; Punto ordinario): Page 2 of 2
Solapas principales
[adsense:336x280:9156825571]
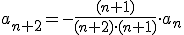
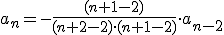
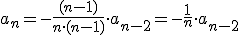
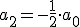
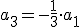
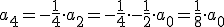
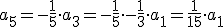
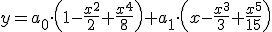
Programa en Sagemath para comprobar los desarrollos en serie de potencias de la ecuacion diferencial
sage: var('x a0 a1')
sage: g=[a0,a1]
sage: y=g[0]+g[1]*x
n=5
sage: for i in range(2,n):
sage: a=-(1/i)*g[i-2]
sage: g.append(a)
sage: for i in range(2,n):
sage: y=g[i]*x^i+y
sage: r=diff(y,x,x)+x*diff(y,x)+y
sage: r.expand(),y
Resultado de la ecuacion diferencial:
(2/5*a1*x^5 + 5/8*a0*x^4, 1/15*a1*x^5 + 1/8*a0*x^4 - 1/3*a1*x^3 -
1/2*a0*x^2 + a1*x + a0)
Que se puede considerar practicamente cero cuanto mas elevemos el valor de n tendiendolo hacia el infinito
Español
google+:



Añadir nuevo comentario